Imagine a sleek, futuristic car with the iconic Apple logo on its hood. A vehicle that combines cutting-edge technology, minimalist design, and the seamless integration of Apple’s ecosystem. For years, this was the dream of the Apple Car, a project that promised to revolutionize the automotive industry. But in 2024, after a decade of development and an estimated $10 billion spent, Apple officially pulled the plug on its ambitious car project, codenamed Project Titan.
What went wrong? How did one of the most valuable companies in the world, known for its innovation and execution, fail to deliver on such a high-profile project? This is the story of the Apple Car—a tale of ambition, missteps, and ultimately, a $10 billion failure.
The Dream: Why Apple Wanted to Build a Car
Apple’s interest in the automotive industry wasn’t just about building a car. It was about redefining transportation.
The Vision
Apple saw the car as the next frontier for its ecosystem. Imagine an iPhone on wheels—a vehicle that could sync with your Apple devices, offer autonomous driving, and provide a seamless user experience. This vision aligned with Apple’s core philosophy of creating products that are both functional and beautiful.
The Timing
The early 2010s were a pivotal moment for the automotive industry. Electric vehicles (EVs) were gaining traction, thanks to Tesla’s success, and autonomous driving technology was advancing rapidly. Apple, always looking for the next big thing, saw an opportunity to disrupt the market.
The Reality: Challenges from Day One
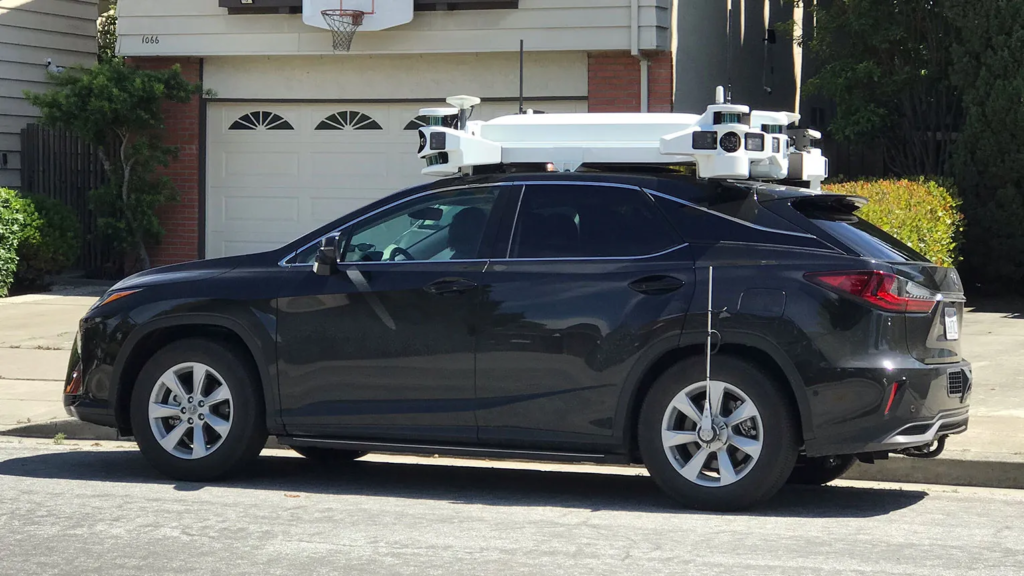

While the vision was compelling, the execution was anything but smooth. Project Titan faced numerous challenges, both internal and external.
Leadership Turmoil
One of the biggest hurdles was leadership instability. Over the years, the project saw multiple changes in leadership, each with a different vision for the car. Some leaders pushed for a fully autonomous vehicle, while others favored a more traditional EV with advanced features. This lack of direction created confusion and delays.
Technical Difficulties
Building a car is vastly different from building a smartphone or a laptop. Apple underestimated the complexity of automotive engineering, from battery technology to safety regulations. For example, developing a reliable autonomous driving system proved to be far more challenging than anticipated.
Cultural Clash
Apple’s secretive, design-driven culture clashed with the collaborative, engineering-heavy nature of the automotive industry. Partnerships with established car manufacturers, such as BMW and Hyundai, fell apart due to disagreements over data sharing and control.
The Cost: A $10 Billion Experiment
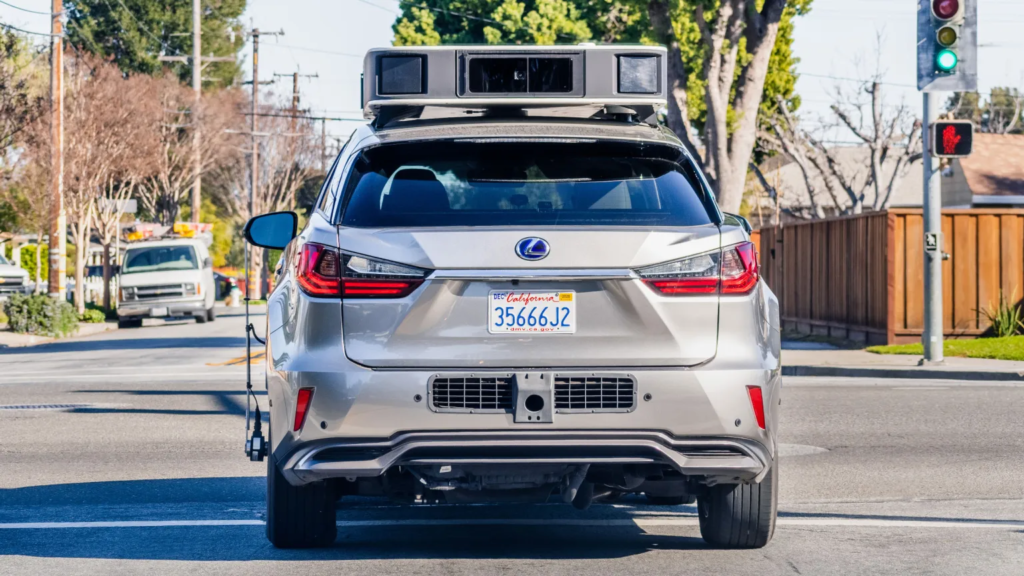

By the time Apple decided to cancel Project Titan, the company had reportedly spent around $10 billion on the project. Where did all that money go?
Research and Development
A significant portion of the budget was allocated to R&D. Apple invested heavily in autonomous driving technology, hiring top talent from companies like Tesla, Google, and Ford. The company also acquired several startups specializing in AI, mapping, and sensor technology.
Testing and Prototyping
Apple built numerous prototypes, ranging from modified Lexus SUVs to custom-designed vehicles. These prototypes were tested extensively, but none met Apple’s high standards for performance and design.
Infrastructure and Partnerships
Apple also spent money on building infrastructure, such as test tracks and data centers, and exploring partnerships with suppliers and manufacturers. However, these efforts often led to dead ends.
The Competition: Why Apple Couldn’t Keep Up
While Apple was struggling to get its car off the ground, competitors were racing ahead.
Tesla’s Dominance
Tesla had a head start in the EV market and was already producing vehicles at scale. By the time Apple entered the scene, Tesla had established itself as the leader in both EVs and autonomous driving technology.
Traditional Automakers
Companies like Ford, General Motors, and Volkswagen were also investing heavily in EVs and autonomous driving. Unlike Apple, these companies had decades of experience in automotive manufacturing and supply chain management.
Tech Giants
Google’s Waymo and Amazon’s Zoox were making significant strides in autonomous driving, further intensifying the competition.
The Fallout: What Went Wrong?
So, why did Apple ultimately decide to cancel Project Titan?
Shifting Priorities
Under CEO Tim Cook, Apple has always been cautious about entering new markets. With the car project facing endless delays and mounting costs, the company decided to focus on its core products, such as the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch, as well as emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR).
Market Realities
The EV market is becoming increasingly crowded, with slim profit margins and intense competition. Apple likely realized that it would be difficult to achieve the same level of success in the automotive industry as it has in consumer electronics.
Lessons Learned
While the Apple Car may have failed, the project wasn’t a total loss. Apple gained valuable expertise in AI, machine learning, and sensor technology, which could be applied to other products, such as AR glasses or home robotics.
The Legacy: What’s Next for Apple?
Although the Apple Car is no more, its legacy lives on.
Focus on Software
Apple is reportedly shifting its focus to developing software for autonomous vehicles, rather than building its own car. This could include infotainment systems, mapping technology, or even a full-fledged autonomous driving platform.
Augmented Reality
Apple’s work on AR could lead to new products that integrate with vehicles, such as AR headsets for navigation or entertainment.
Sustainability
Apple’s commitment to sustainability could also influence the automotive industry. The company’s expertise in battery technology and renewable energy could be applied to EVs or other green technologies.
A Bold Dream, a Costly Failure
The Apple Car was a bold dream that captured the imagination of millions. But in the end, it was a dream that proved too difficult to realize. Despite its $10 billion investment, Apple couldn’t overcome the challenges of entering a complex and competitive industry.
Yet, failure is often a stepping stone to success. The lessons learned from Project Titan could pave the way for future innovations, ensuring that Apple remains at the forefront of technology.
As for the Apple Car, it will go down in history as a $10 billion experiment—a reminder that even the most ambitious dreams can sometimes fall short.