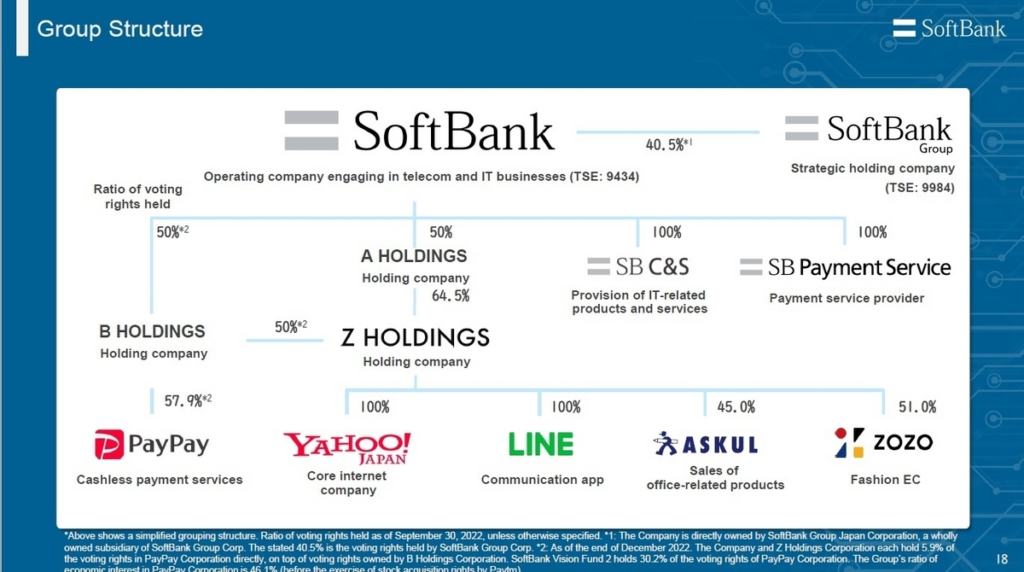
When you think of companies shaping the future of technology, names like Apple, Google, and Amazon might come to mind. But there’s another player that’s been quietly (and sometimes loudly) influencing the global tech landscape: SoftBank. From its humble beginnings as a software distributor in Japan to becoming one of the world’s most influential investment firms, SoftBank’s journey is nothing short of extraordinary.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what SoftBank is, how it became a tech powerhouse, and why it matters in today’s fast-paced world of innovation. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an investor, or just curious about the forces driving the future, this guide will give you a clear understanding of SoftBank’s role in the global economy.
What is SoftBank? A Brief Overview
The Origins of SoftBank
SoftBank was founded in 1981 by Masayoshi Son, a visionary entrepreneur with a knack for spotting opportunities. Starting as a software distributor in Japan, the company quickly expanded into publishing, telecommunications, and eventually, venture capital.
Today, SoftBank is a multinational conglomerate with interests in technology, energy, finance, and more. But what truly sets it apart is its role as a global investor, backing some of the most innovative companies in the world.
SoftBank’s Core Businesses
SoftBank operates through several key divisions:
SoftBank Group Corp: The parent company overseeing its diverse portfolio.
SoftBank Vision Fund: A $100 billion investment fund focused on tech startups.
SoftBank Mobile: One of Japan’s largest mobile carriers.
ARM Holdings: A leading semiconductor and software design company.
The Rise of SoftBank: From Software to Superpower
Masayoshi Son: The Visionary Behind SoftBank
No discussion about SoftBank is complete without mentioning Masayoshi Son. Often compared to figures like Steve Jobs and Elon Musk, Son is known for his bold vision and high-risk, high-reward strategies.
Son’s early investments in companies like Yahoo and Alibaba paid off massively, cementing SoftBank’s reputation as a savvy investor. His dream of creating a “300-year company” has driven SoftBank’s aggressive expansion into cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, robotics, and renewable energy.
Key Milestones in SoftBank’s Journey
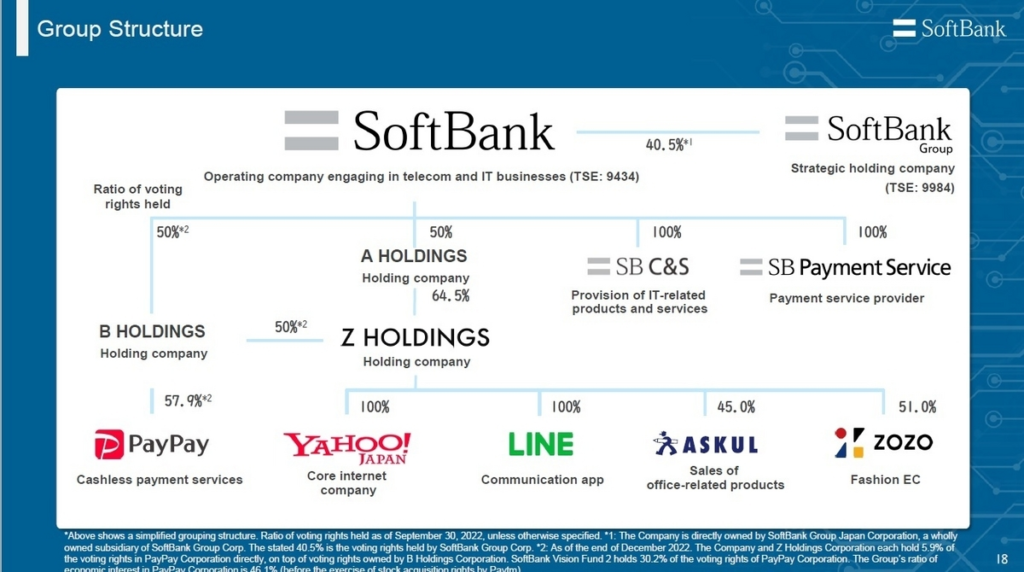
1980s: SoftBank starts as a software distributor and expands into publishing.
1990s: Invests in early internet companies like Yahoo and E*TRADE.
2000s: Acquires Vodafone Japan, becoming a major player in telecommunications.
2010s: Launches the SoftBank Vision Fund, the largest tech investment fund in history.
2020s: Focuses on AI, robotics, and sustainability through strategic investments.
The SoftBank Vision Fund: A Game-Changer in Tech Investment
What is the SoftBank Vision Fund?
The SoftBank Vision Fund is a $100 billion investment fund launched in 2017. Backed by sovereign wealth funds, corporations, and private investors, it’s the largest tech investment fund ever created.
The fund’s goal is to identify and support the next generation of tech giants, with a focus on AI, IoT, and other transformative technologies.
Notable Investments by the Vision Fund
The Vision Fund has invested in some of the most high-profile startups and tech companies, including:
Uber: The ride-hailing giant that revolutionized transportation.
WeWork: The coworking space company (though this investment faced significant challenges).
ByteDance: The parent company of TikTok, the viral video-sharing app.
ARM Holdings: A leader in semiconductor design, acquired by SoftBank in 2016.
The Impact of the Vision Fund
The Vision Fund has reshaped the tech investment landscape, providing startups with unprecedented levels of funding. However, it has also faced criticism for inflating valuations and encouraging unsustainable growth.
SoftBank’s Role in Shaping the Future
Investing in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
SoftBank is betting big on AI and robotics, believing these technologies will drive the next wave of innovation. Its investments in companies like Boston Dynamics and its own Pepper robot highlight this focus.
Renewable Energy and Sustainability
Through its SB Energy division, SoftBank is investing in solar and wind energy projects worldwide. This aligns with its broader vision of creating a sustainable future.
The ARM Acquisition: A Strategic Move
In 2016, SoftBank acquired ARM Holdings, a UK-based company that designs chips for nearly every smartphone in the world. This acquisition positions SoftBank at the heart of the semiconductor industry, a critical component of modern technology.
Challenges and Controversies

The WeWork Debacle
One of SoftBank’s most high-profile missteps was its investment in WeWork. The coworking startup’s failed IPO and subsequent valuation drop led to significant losses for SoftBank and raised questions about its investment strategy.
High-Risk, High-Reward Strategy
SoftBank’s aggressive approach to investing has yielded both spectacular successes and notable failures. While some investments have paid off handsomely, others have struggled to deliver returns.
Regulatory Scrutiny
As SoftBank’s influence grows, it has faced increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide. Concerns about market dominance and the impact of its investments on competition have led to calls for greater oversight.
Lessons from SoftBank’s Journey
The Power of Vision and Ambition
SoftBank’s success is a testament to the power of bold vision and relentless ambition. Masayoshi Son’s willingness to take risks has propelled the company to new heights.
The Importance of Adaptability
In the fast-paced world of technology, adaptability is key. SoftBank’s ability to pivot from software distribution to telecommunications to venture capital highlights the importance of staying ahead of trends.
Balancing Risk and Reward
SoftBank’s journey also serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between risk and reward. While high-risk investments can yield massive returns, they can also lead to significant losses.
Conclusion: What Does SoftBank Mean for the Future?
SoftBank is more than just a company—it’s a force shaping the future of technology and innovation. From its early days as a software distributor to its current role as a global investor, SoftBank has consistently pushed the boundaries of what’s possible.
As we look to the future, SoftBank’s influence will undoubtedly continue to grow. Whether through its investments in AI, robotics, or renewable energy, SoftBank is playing a pivotal role in building the world of tomorrow.
FAQs About SoftBank
- What does SoftBank do?
SoftBank is a multinational conglomerate with interests in technology, telecommunications, and venture capital. It’s best known for its SoftBank Vision Fund, which invests in tech startups. - Who owns SoftBank?
SoftBank is a publicly traded company, but its founder, Masayoshi Son, remains a significant shareholder and the driving force behind its vision. - What is the SoftBank Vision Fund?
The SoftBank Vision Fund is a $100 billion investment fund focused on supporting innovative tech companies, particularly in AI, IoT, and other transformative technologies. - What are some of SoftBank’s most notable investments?
SoftBank has invested in companies like Uber, WeWork, ByteDance (TikTok’s parent company), and ARM Holdings. - What challenges has SoftBank faced?
SoftBank has faced challenges such as the WeWork debacle, regulatory scrutiny, and criticism of its high-risk investment strategy.
By understanding SoftBank’s journey, we gain valuable insights into the forces shaping the future of technology and innovation. Whether you’re an investor, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the world of business, SoftBank’s story is one worth knowing.