TikTok, the wildly popular short-form video app owned by Chinese tech giant ByteDance, has been embroiled in a high-stakes controversy in the United States for over four years. At the heart of the issue are concerns about national security and user data privacy, with fears that the Chinese government could access sensitive information from American users. This ongoing drama has led to legal battles, political maneuvering, and a potential sale of TikTok’s U.S. operations. Here’s an in-depth look at the key events, the current status, and what the future might hold for TikTok in the U.S.
The Rise of TikTok and Its Data Privacy Concerns
Since its global launch in 2018, TikTok has become a cultural phenomenon, boasting over 150 million active users in the U.S. alone. However, its Chinese ownership has raised red flags among U.S. lawmakers and regulators. Critics argue that ByteDance could be compelled to share user data with the Chinese government under China’s national security laws. TikTok has consistently denied these allegations, emphasizing that it stores U.S. user data on American servers and complies with local laws.
Despite these assurances, the U.S. government has taken significant steps to address these concerns, leading to a series of legal and political showdowns.
A Timeline of TikTok’s U.S. Controversy
The TikTok saga began in August 2020 when then-President Donald Trump signed an executive order to ban transactions with ByteDance, citing national security risks. This was followed by an attempt to force the sale of TikTok’s U.S. operations to an American company. Tech giants like Microsoft, Oracle, and Walmart emerged as potential buyers, but the deal was put on hold after a U.S. judge temporarily blocked Trump’s executive order.
The situation evolved under the Biden administration. In April 2024, the U.S. Senate passed the Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act (PAFACA), commonly known as the “TikTok ban.” President Joe Biden signed the bill into law, requiring TikTok to either divest its U.S. operations or face a ban. TikTok responded by suing the U.S. government, arguing that the ban violated the First Amendment rights of its users and the company itself.
Trump’s Surprising Reversal and the 75-Day Reprieve
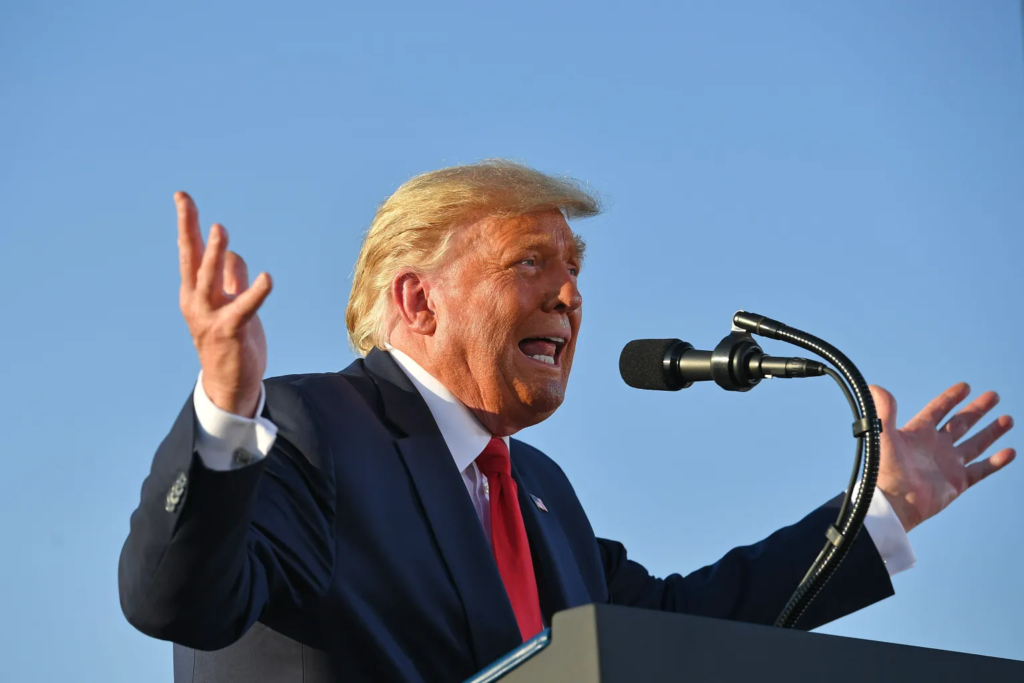

In a surprising twist, former President Donald Trump, who initially spearheaded the push to ban TikTok, changed his stance in late 2024. On December 27, 2024, Trump opposed the ban in a court filing, suggesting he could find a way to keep the app operational in the U.S. This marked a significant shift from his earlier position.
On January 20, 2025, Trump signed an executive order granting TikTok a 75-day extension to either sell a stake in its U.S. operations or negotiate a deal. His goal is to establish a 50-50 ownership structure between ByteDance and a U.S.-based company. This extension has kept TikTok alive in the U.S. for now, but its future remains uncertain.
The Battle for TikTok: Who’s in the Running?

Several investor groups and companies have expressed interest in acquiring TikTok’s U.S. operations, with valuations estimated to exceed $60 billion. Here’s a look at the key players:
- The People’s Bid for TikTok
- Led by Frank McCourt, former owner of the Los Angeles Dodgers, this consortium aims to prioritize user privacy and data control.
- Notable supporters include Reddit co-founder Alexis Ohanian, investor Kevin O’Leary, and Tim Berners-Lee, inventor of the World Wide Web.
- Jesse Tinsley’s Consortium
- The CEO of Employer.com is leading a group of American investors with a $30 billion all-cash offer.
- Participants include Roblox CEO David Baszucki and YouTube star MrBeast.
- Oracle
- The tech giant has reemerged as a top contender, with co-founder Larry Ellison expressing interest in a 50% ownership deal.
- Other Potential Buyers
- Former Activision CEO Bobby Kotick, ex-Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin, and retail giant Walmart are also in the mix.
TikTok’s Temporary Shutdown and Comeback
In January 2025, TikTok briefly went dark in the U.S. following the enactment of PAFACA. However, the app was back online within 12 hours, thanks to Trump’s intervention. This rollercoaster episode highlighted the app’s resilience and the complexities of its legal and political challenges.
What’s Next for TikTok?
As of March 2025, TikTok’s fate hangs in the balance. While no definitive deal has been reached, negotiations are ongoing, and a resolution could be announced soon. The platform’s massive user base and influence make it a highly coveted asset, but its Chinese ties continue to complicate matters.
For now, TikTok remains operational in the U.S., but its long-term future depends on whether ByteDance can strike a deal that satisfies U.S. regulatory requirements.
Why This Matters for Users and Investors

The TikTok controversy underscores the growing tension between technology, national security, and free speech. For users, the potential ban or sale raises questions about data privacy and access to a beloved platform. For investors, TikTok represents a lucrative opportunity to tap into a thriving social media ecosystem.
As the drama unfolds, one thing is clear: TikTok’s journey in the U.S. is far from over. Stay tuned for updates on this high-stakes battle that could reshape the tech and social media landscape.
Key Takeaways
- TikTok’s U.S. operations are at the center of a national security debate, with concerns over data privacy and Chinese government access.
- Legal battles and political negotiations have kept the app in limbo, with a potential sale or ban on the horizon.
- Several high-profile investors and companies are vying to acquire TikTok, with valuations exceeding $60 billion.
- The outcome of this saga will have far-reaching implications for users, investors, and the tech industry as a whole.
By staying informed about TikTok’s evolving situation, you can better understand the intersection of technology, politics, and privacy in today’s digital age.