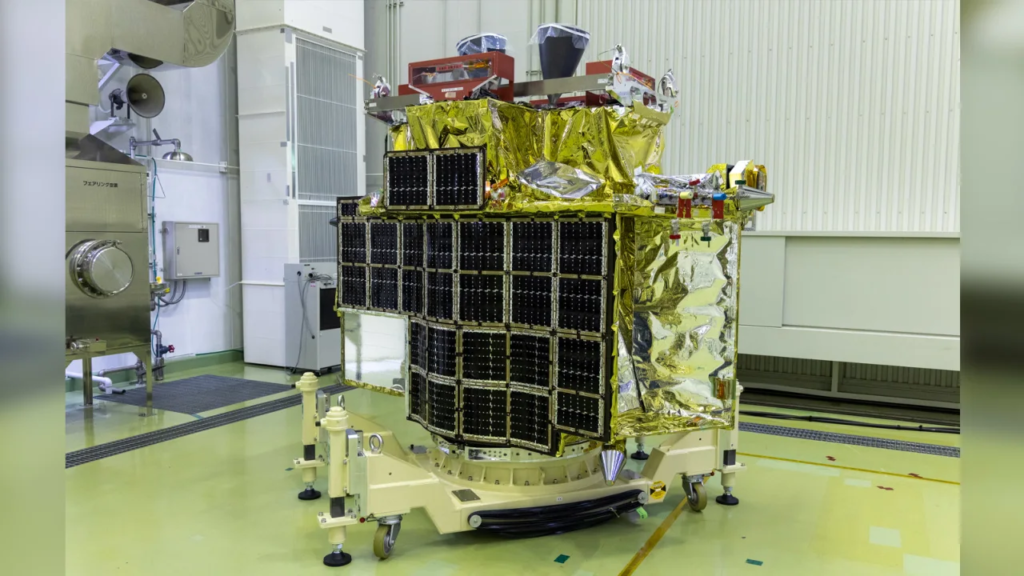
A groundbreaking satellite aimed at revolutionizing our understanding of celestial objects, and a lunar lander known as the “Moon Sniper,” embarked on a momentous journey on Wednesday night.
The Japanese Space Agency (JAXA) launch, after several weather-related delays, took place aboard an H-IIA rocket from the Tanegashima Space Center at 7:42 p.m. ET on Wednesday or 8:42 a.m. Japan Standard Time on Thursday.

The event was streamed live on JAXA’s YouTube channel, providing viewers with broadcasts in both English and Japanese.
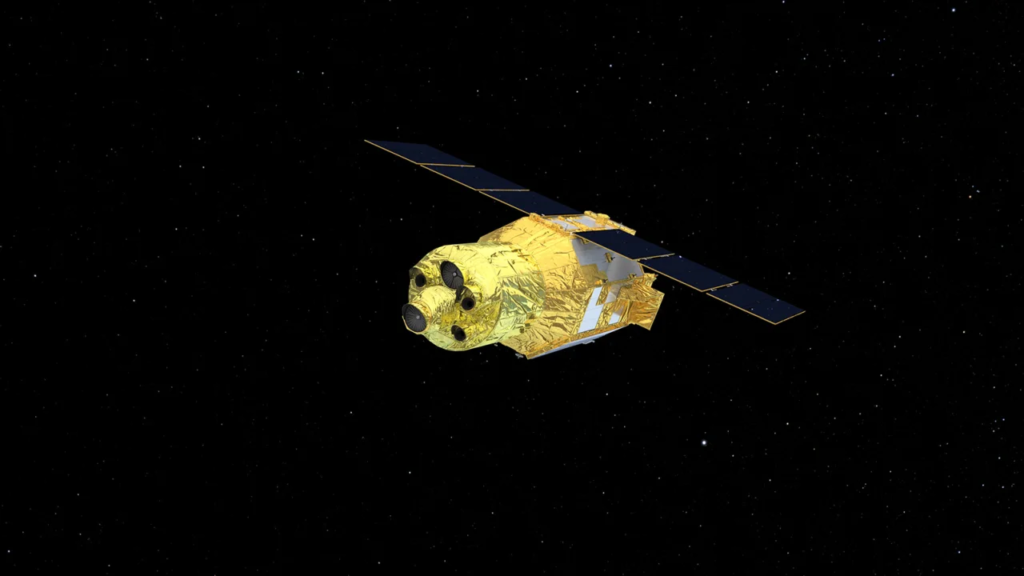
The satellite, officially named XRISM (pronounced “crism”), short for X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, is a collaborative endeavor between JAXA and NASA, with contributions from the European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency.
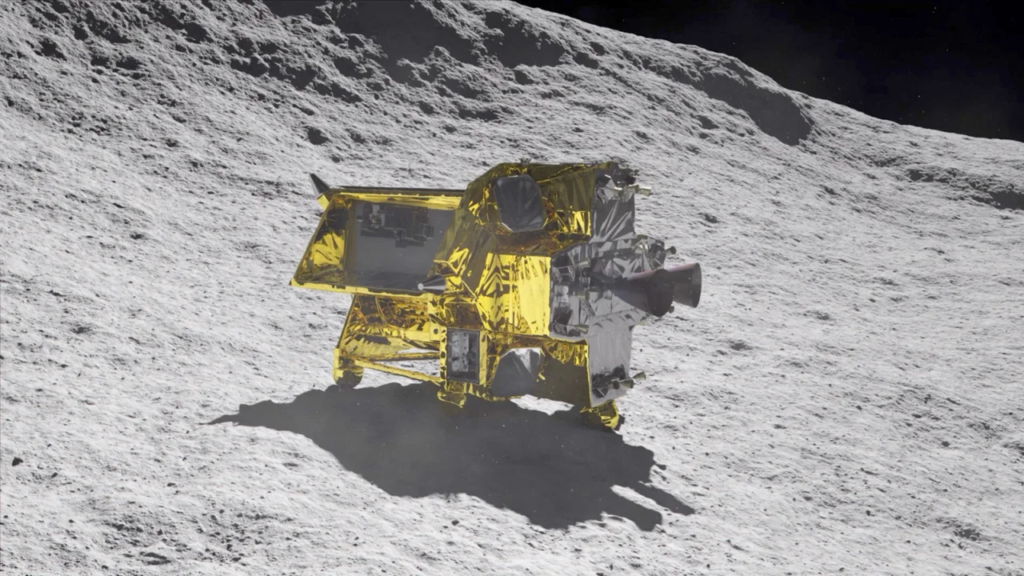
Accompanying XRISM is JAXA’s SLIM, or Smart Lander for Investigating Moon. This compact lunar lander is engineered to demonstrate an extremely precise landing within 100 meters (328 feet), as opposed to the typical kilometer range, utilizing high-precision landing technology. This remarkable precision earned the mission its moniker, “Moon Sniper.”
According to NASA, the satellite and its two instruments will focus on observing the universe’s hottest regions, largest structures, and objects with the most substantial gravitational forces. XRISM’s primary function is to detect X-ray light, a wavelength that is invisible to the human eye.
X-rays are emitted by some of the most energetic objects and events in the cosmos, which is why astronomers are eager to study them.
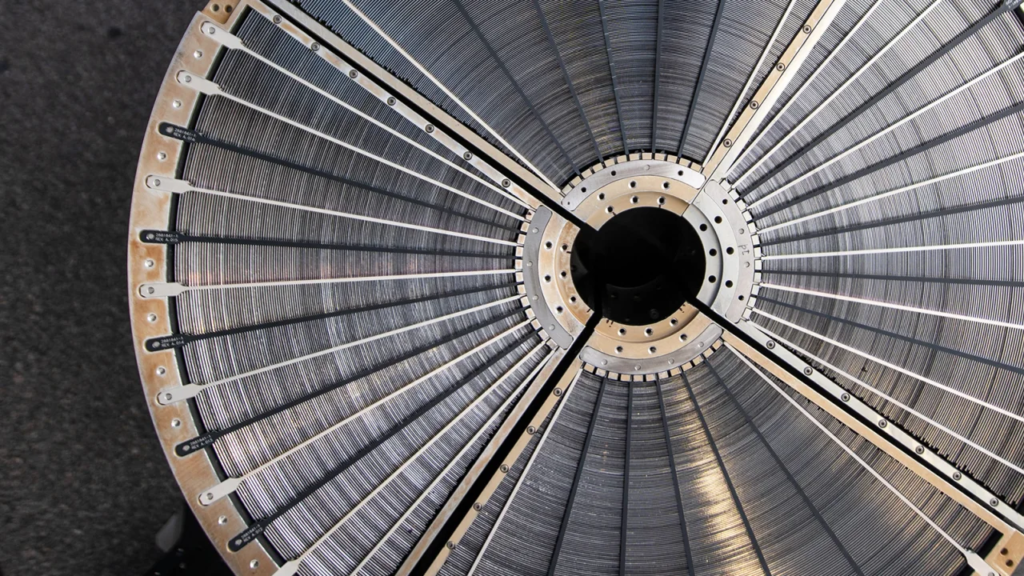
The satellite is equipped with thousands of curved, nested mirrors specifically designed for detecting X-rays, in contrast to other wavelengths of light. Upon reaching orbit, XRISM will require several months of calibration. The mission is designed to operate for three years.

XRISM is capable of detecting X-rays with energies ranging from 400 to 12,000 electron volts, significantly beyond the energy levels of visible light, which typically ranges from 2 to 3 electron volts, according to NASA. This broad range of detection will enable the study of cosmic phenomena across the universe.
The satellite houses two instruments: Resolve and Xtend. Resolve tracks minute temperature fluctuations to determine the source, composition, motion, and physical state of X-rays. Resolve operates at a chilling temperature of minus 459.58 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 273.10 degrees Celsius), approximately 50 times colder than deep space, thanks to a container of liquid helium.
This instrument will enable astronomers to unlock the mysteries of cosmic phenomena, including the chemical details of hot gas within galactic clusters.
Meanwhile, Xtend provides XRISM with one of the most extensive fields of view on an X-ray satellite.
“The spectra XRISM collects will be the most detailed we’ve ever seen for some of the phenomena we’ll observe,” said Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM project scientist at Goddard. “The mission will provide us with insights into some of the most difficult places to study, like the internal structures of neutron stars and near-light-speed particle jets powered by black holes in active galaxies.”
In parallel, SLIM will employ its own propulsion system to embark on a journey toward the moon. The spacecraft will reach lunar orbit approximately three to four months after launch, orbit the moon for one month, and then begin its descent, aiming for a soft landing within four to six months after launch. If the lander achieves its goal, it will also conduct a brief study of the lunar surface.

Unlike recent lunar lander missions that have targeted the moon’s south pole, SLIM has set its sights on a location near a small lunar impact crater called Shioli, near the Sea of Nectar. Here, it will investigate rock compositions that could help scientists uncover the moon’s origins. The chosen landing site is just south of the Sea of Tranquility, where Apollo 11 made its historic landing near the moon’s equator in 1969.
Achieving precise landings on the moon is a significant goal for JAXA and other space agencies, particularly in resource-rich areas such as the lunar south pole, where permanently shadowed regions contain water ice, and numerous hazards like craters and rocks must be navigated. Future missions will require pinpoint landings to avoid these obstacles.
Moreover, SLIM’s lightweight design holds promise for agencies planning more frequent missions and exploring the moons of other planets, such as Mars. If SLIM achieves its objectives, JAXA believes it will revolutionize missions from “landing where we can” to “landing where we want.”