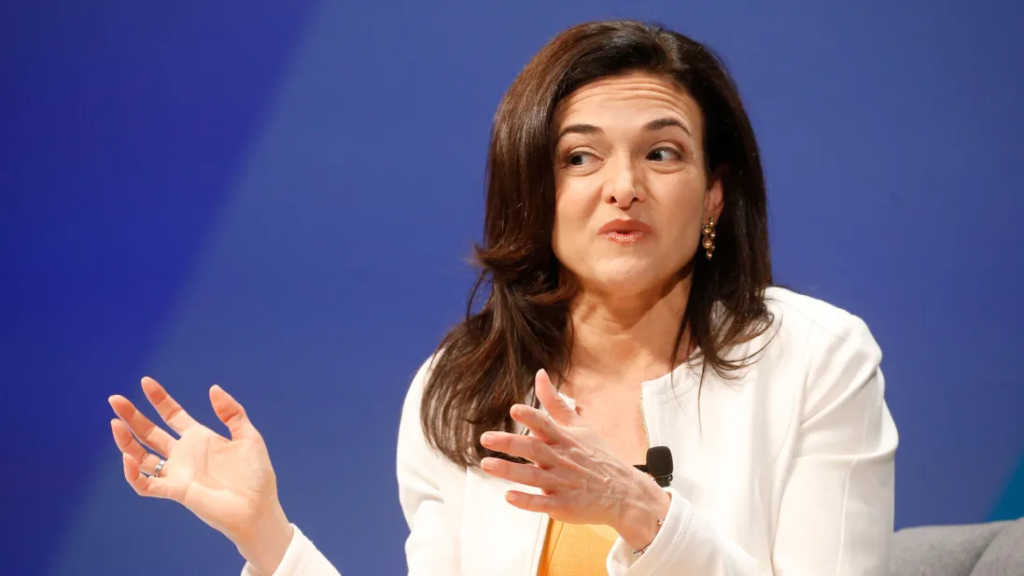
Sheryl Sandberg, the former Chief Operating Officer (COO) of Meta and a former board member, has been sanctioned by a Delaware court for allegedly deleting emails connected to the Cambridge Analytica privacy scandal. This decision highlights ongoing legal concerns regarding Meta’s handling of user data and the responsibilities of its leadership.
The Case Against Sandberg
The sanctions arise from a lawsuit filed by Meta shareholders in 2022 against Sandberg and Jeff Zients, another former Meta board member. The lawsuit alleges that the two executives used personal email accounts to discuss matters related to a 2018 shareholder lawsuit. That lawsuit had accused Facebook (now Meta) of breaching its fiduciary duties and failing to protect user privacy.
The plaintiffs further alleged that Sandberg and Zients deleted emails from their personal accounts despite explicit court orders to preserve them. According to the Delaware judge presiding over the case, these allegations appear credible. The court pointed to Sandberg’s use of a pseudonym on her personal Gmail account to discuss issues relevant to the legal proceedings.
The judge also criticized Sandberg’s legal team for not providing clear answers during the discovery process. This has led to the inference that Sandberg manually deleted emails, rather than relying on automatic deletion functions.
Impact of the Sanctions
As part of the sanctions, the court has increased the burden of proof required for Sandberg’s defense. She must now provide “clear and convincing evidence” to support her claims— a higher standard than the typical “preponderance of evidence” used in civil cases.
The court also awarded certain legal expenses to the plaintiffs, further complicating Sandberg’s legal standing in this case.
Sandberg’s Response
A spokesperson for Sheryl Sandberg has dismissed the allegations, stating that the claims brought against her “have no merit.” However, the sanctions from the court indicate serious concerns about her actions during the discovery process.
The Context: Cambridge Analytica and Facebook’s Privacy Failures
This legal dispute ties back to broader allegations against Facebook regarding its failure to safeguard user data. In 2012, Facebook reached an agreement with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to stop collecting and sharing user data without explicit consent. However, the company was later accused of violating this agreement by continuing to share personal data with commercial entities, including Cambridge Analytica.
Cambridge Analytica notoriously harvested data from millions of Facebook users without their consent to influence political campaigns, including the 2016 U.S. presidential election. These revelations triggered widespread public outrage, regulatory scrutiny, and lawsuits against Facebook.
In 2019, Meta resolved some of these issues by agreeing to pay a $5 billion fine to the FTC—one of the largest penalties in U.S. history for privacy violations. The company also faced significant financial penalties from regulators in Europe.
Concerns Surrounding Sheryl Sandberg’s Role
As a prominent leader at Facebook during the height of the Cambridge Analytica scandal, Sandberg’s involvement raises ethical and legal questions.
Use of Personal Email Accounts: The use of personal accounts for company-related communications is seen as a potential breach of corporate governance standards, undermining transparency and accountability.
Alleged Email Deletion: The accusations of deleting emails despite court orders suggest an effort to obscure critical evidence, which has serious legal implications.
Leadership Responsibility: As COO, Sandberg held a significant role in shaping Facebook’s policies. This case raises questions about her accountability for the company’s failures to uphold user privacy.
What’s Next for Sandberg and Meta?
Sandberg faces significant legal challenges due to the increased burden of proof imposed by the court. Proving her defense with clear and convincing evidence will require substantial documentation and transparency.
For Meta, this case is another reminder of the lingering consequences of the Cambridge Analytica scandal. Although the company has implemented changes to improve privacy protections and compliance, legal and reputational issues continue to affect its operations and leadership.
The sanctioning of former Meta COO Sheryl Sandberg underscores the importance of accountability at the highest levels of leadership. As the case unfolds, it highlights critical issues surrounding data privacy, corporate governance, and the responsibilities of executives in safeguarding user trust. For both Sandberg and Meta, this legal battle serves as a cautionary tale about the long-term consequences of privacy missteps in the digital age.